Surgery & Outcome
Randomization and Enrollment
All patients scheduled for CABG at the study centers will be screened for inclusion. Eligible patients who provide informed consent can be enrolled. Each center will keep a log of all screened patients with details on inclusion or reasons for exclusion.
Randomization will be performed through a web-based randomization system. A confirmation e-mail with the details of the randomization will be sent to the contacts investigators of the single centers, the lead PI and the Data Monitoring and Analyzing Committee at the moment of randomization.
Patients will be randomized in a 1:1 fashion between the two groups: Single Arterial Graft (SAG) and Multiple Arterial Grafts (MAG). Randomization will be stratified by the center (NOT the individual surgeon) and the type of second arterial graft used to provide treatment distribution in equal proportion.
Surgical Procedures
- In all cases one ITA will be anastomosed to the LAD.
- For patients randomized to the SINGLE ARTERIAL GRAFT group, SVG grafts will be used for all non-LAD target vessels.
- For patients randomized to the MULTIPLE ARTERIAL GRAFT group, the second ITA or the RA will be used to graft the main target vessel of the circumflex distribution.
- Identification of the second ITA or RA target will be based on coronary angiography and will be left to the judgement of the operating surgeon.
- The choice between second ITA and RA will be decided by the individual surgeon. The use of RAs previously submitted to catheterization for diagnostic or interventional procedures is strongly discouraged. For the use of RA grafts, a high-grade stenosis of the coronary target is highly recommended. A moderate stenosis is sufficient for the right ITA.
- The use of supplementary Arterial Grafts will be allowed ONLY in the MULTIPLE ARTERIAL GRAFT group. For right coronary targets, a high-grade target vessel stenosis is recommended for both the RA and RITA.
- The use of the right gastroepiploic artery (RGEA) as third Arterial Graft will be allowed in the MULTIPLE ARTERIAL GRAFT group. The use of the RGEA will be allowed only if the operating surgeon has a personal experience of at least 250 cases using the RGEA. It is recommended that the RGEA be used to graft vessels of the inferior wall with > 90% stenosis and is harvested in a skeletonized fashion.
- Proximal aortic anastomosis and conventional harvesting technique (open or endoscopic) are required for SV grafts.
Graft Assessment
The intraoperative assessment of graft patency using transit time flowmeter is a class IIA recommendation, level of evidence C of the Task Force on Myocardial Revascularization of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). The assessment of graft patency is not mandated as part of the protocol, but it is recommended.
Postoperative assessment of graft patency will be performed in those centers where this is the standard of care, using the method routinely used in those centers. The criteria used for the definition of graft status are summarized in the Appendix. Results of the patency studies when available will be entered in the case report form.
Secondary Prevention
Details of secondary prevention will be left at the discretion of the individual center. The use of evidence-based medication, including aspirin, statins, beta-blockers, and ACE-inhibitors is strongly recommended.
The use of dual antiplatelet therapy is recommended for 3 months after off-pump procedures, coronary endarterectomy or angioplasty and for 1 year in acute coronary syndromes.
Patient Follow-up
- Patients will be seen in clinic postoperatively as per institutional routine. Subsequent follow-up will be performed at 6 months postoperatively and every 6 months thereafter by telephone.
- Follow-up for all the randomized subjects will continue for 10 years.
- Details on current medications, clinical status, clinical events, re-hospitalization and revascularization will be recorded. For patients who have been or are hospitalized, hospital records and/or a death certificate will be acquired if possible. Follow-up case report forms will be completed; additional specific study forms will be completed for patients who experience one or more study events.
Outcome Measures
Primary
The primary outcome will be a composite of death from any cause, any stroke, post-discharge myocardial infarction and/or repeat revascularization.
Secondary
The secondary outcome will be all-cause mortality
Safety
The primary safety outcomes will be a composite of death from any cause, any stroke, and any myocardial infarction
Secondary safety outcomes will be major postoperative complications
Sample Size Calculations
Incidence of outcomes in the major contemporary RCTs including CABG patients.
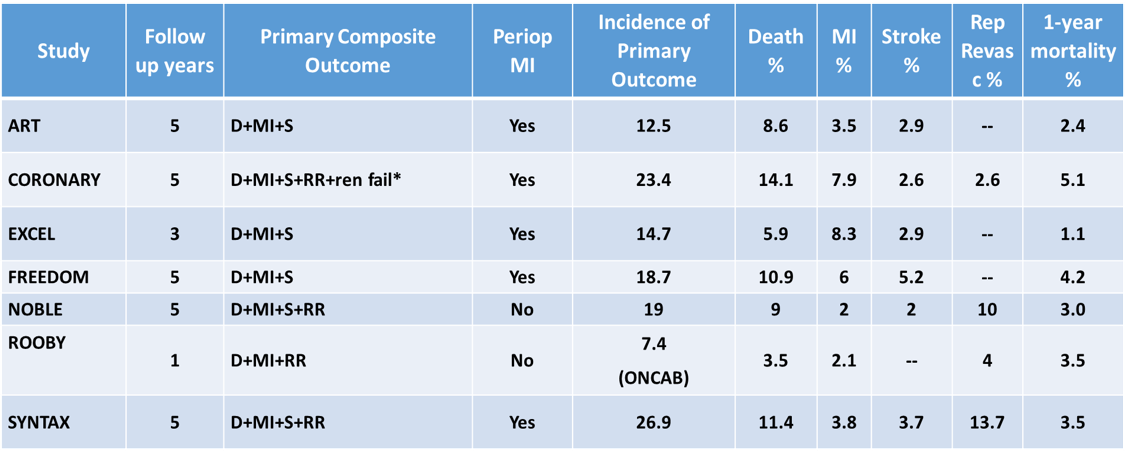
- ROMA is an event-driven trial
- A 17% control event rate is consistent with the event rates in the table. In order to detect a 20% relative reduction (from 17% to 14.2%) in the primary outcome, with 90% power at 5% two-sided alpha and assuming a time to event analysis, the sample size must include 3650 patients or 845 events.
- On the basis of the 1 and 5 year data of the published RCTs:
- Linearized rate of death of 1.5-2% between year 1 and 5 was observed. We estimate that the 5 year mortality in ROMA will be 8-10%.
- Linearized rate of death of 2% between 5 and 10 years postoperatively can be assumed. We estimate that the overall 10 year mortality in ROMA will be 18-20%.
- In order to detect a 20% relative reduction (from 18% to 14.4%) in 10-year mortality, with 80% power at 5% alpha, the sample size must include 3650 patients or 631 events
- Considering 5% crossover/protocol violation and up to 10% loss to follow-up at 10 years postoperatively, a conservative estimate is that 4300 patients are required.
- The primary outcome analysis will be performed after 845 events. This will likely happen at a median of 5 years of follow up (minimum 3 years)
- The secondary outcome analysis will be performed after 631 events. This will likely happen at a median of 10 years of follow up (minimum 7 years)
- The aim of the trial is to enroll at least 4300 patients in at least 25 centers in the US, Canada, Europe, and Asia. Assuming an enrollment rate of 1 patient/center/week, 3 ½ – 4 years will be necessary to complete the enrollment phase.
- In case of funding we assume to have about 50 centers for the main trial, so that the duration of the enrollment phase will be shorter or unchanged even in case of a lower enrollment rate.
